
How to File an IRS Form 1040: A Step-Wise Guide
March has arrived, and you have more than 40 days to file your income tax forms. After that, it’s time to pay the IRS and claim certain tax credits/refunds. If you are an Indian citizen in the United States or a US resident, we can show you how to fill out the 1040 form in simple steps.
Recommended: New to the US – Here’s what you need to know about filing your taxes as an NRI in the US –
What Exactly is a 1040 Form?
1040 is a tax form used by United States residents to file their federal income taxes annually. Hence, it’s essential to know how to fill out 1040. The form aids in calculating annual income and the claim on deductions and tax credits.
There were multiple variations of 1040 before 2017. However, since the passage of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) in 2017, most Americans have been filling out 1040 forms.
Senior citizens can file Form 1040-SE, while non-residents must file Form 1040-NR.
To complete your 1040 form, you have two options:
- You can either file electronically, known as e-filing.
- Alternatively, you may print the form, fill it out, and mail it to the IRS (Internal Revenue Services).
Compared to manual filing, e-filing is simple, convenient, and quick. In addition, when you e-file your tax returns, you can receive your refund faster. Physical or paper filing takes longer to reach the IRS and delays the refund process.
How to Fill Out a 1040 Form?
Don’t be intimidated looking at the form. Trust us; it’s not that challenging. We provide a step-by-step guide (on the same flow as it is on the form) on how to fill out 1040:
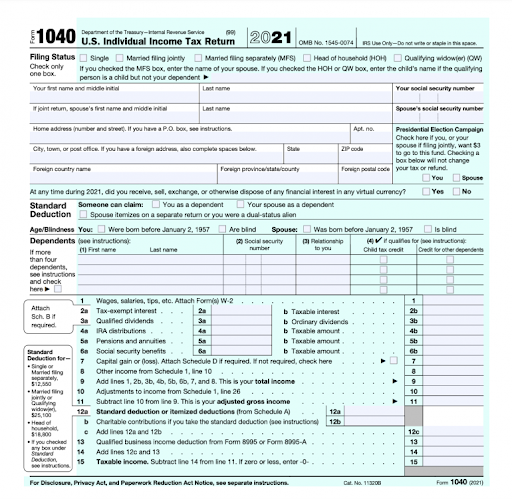
Filing status: It’s essential to specify whether you’re filing your 1040 as a single person, a married couple, filing jointly, or filing separately with your spouse. You can also mention if you are the head of the household or a widower. This will help you take advantage of certain standard deductions based on your status.
Personal information: Fill in your full name, address, and social security number in this field. Whether filing jointly or individually, you must also include additional input about your spouse and dependents.
Election contribution: There’s a neat box in the form that now allows you or your spouse to contribute $3 to the presidential election fund. The money will be equally split between Democrats and Republicans. It would not affect your tax refund or liability.

Cryptocurrency: There is a rise in digital or cryptocurrency as a preferred investment mode. For instance, 46 million Americans are among 300 million cryptocurrency users across the globe. As a result, this feature enables you to declare if you have exchanged cryptocurrency in the previous financial year.
Standard deduction: Your standard deduction eligibility is based on your age, filing status, and whether or not you are blind. Fill in the boxes as applicable. Those who are married and filing jointly with their spouse should also mention if they are financially dependent on another. And if you’re a dual-status alien, you should also mention this in the form.
Dependents: In this section, you may fill in the details about your dependents and seek a tax credit. In this section, you should list your dependents, age, and their relationship with you. You should also mention if you are entitled to a child tax credit or a credit for other dependents.

Calculate taxable income: This section is crucial, and you must fill it in properly. Here is where you list the fruits of your labor from the previous year. This column is where you disclose your earnings from your job. If you are a salaried employee, provide a W-2 form.
Next, simply tick boxes that show your non-employment income, like earned dividends and interest, annuities, pension, IRA tax rebates, social security benefits, and so on. You can find a list of many other deductions on the IRS website.
Calculate your tax liability: Now is the time to count your blessings in the form of tax credits. These are the taxes withheld by your employer. Subtract the tax credits from the total amount you must pay.
The tax bill is the final number. If your tax bill exceeds your tax credits, pay the IRS whenever you file your tax returns. You will receive a refund from the IRS if you have overpaid. If you e-filed, your refund will be directly deposited in your bank account. Otherwise, the IRS will mail you a check.
Schedules
To file your income tax returns, you need a simple 1040 Form. There are separate schedules you attach with 1040 in case of additional income, or if you owe the IRS more money, or you would like to claim extra credit.
These schedules are as follows:
Schedule 1– Fill this schedule if you have earnings from:
- A business (also file form C)
- Alimony payments
- Agricultural income
- Educator expenditures
- Rental income (file form E)
- Health savings account
- Health insurance,
- Retirement contribution deductions
- Student loan or other sources
Schedule 2 – Fill this if you owe the IRS:
- Self-employment tax
- Alternative minimum tax (AMT)
- Household employment tax
- Net investment income tax
- Additional Medicare tax
- Recovery rebate credit because you did not receive a coronavirus stimulus check, an economic impact payment.
Schedule 3 – Use this schedule to claim IRS credits and payments. This includes:
- Foreign tax credits
- Child and dependent care credits
- Education
- General business incentives
- Home energy credits, etc.
Those who cannot file federal tax returns by April 18, 2022, can request an extension and file by October 15, 2022. If you must make payments, do this before the April deadline.
Back taxes: If you owe the IRS money for previous years’ taxes, you must send 1040 to the IRS. In this scenario, e-filing is not possible.
Refunds: After the IRS processes your returns, you will receive your refund in 21 days.
If you follow the instructions given above, you will be able to file your taxes in no time. If you have all of your receipts and supporting documentation, you should be OK.
Recommended: The Ultimate Documents Checklist to File US Income Tax Returns – AOTAX.COM
If you are an Indian resident in the United States and are unsure how to fill out 1040, contact AOTAX. Our team of capable tax advisers and preparers at AOTAX can assist you in meeting your deadlines smoothly.


Recent Comments